“The longer your waistline, the shorter your lifeline”.
A study published in Diabetes Care noted that when diabetic individuals lost around 9-13 kgs, they witnessed a significant increase in their life-span, with an average of 25% reduced mortality. This number is big.
About 80-85% of people with Type 2 diabetes are overweight. Research shows that excess body weight is the most significant cause of Type 2 diabetes.
PhD Nicola Davies writes in Diabetes Self Management, “People with a BMI above 30 are 80 times more likely to develop Type 2 diabetes than people with a BMI under 22.” 80 times. If these numbers don’t wake us up, I don’t know what will.
Let’s first understand the most important hormone for diabetes: Insulin. You might be already aware but let me explain it quickly: Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas in the body and its role is to help the body cells to take in glucose from blood to convert into energy. So, it reduces sugar in the blood and stores it in the cell.
Type 2 diabetes in almost all cases starts with excess insulin in the body. Sometimes, to learn new things, you have to unlearn old things. Keep your mind open.
Dr. Neal Barnard, famous for his book on reversing diabetes, explains with a very simple example what happens in diabetes. Assume you have to open a lock with a key. But the lock does not open. And you investigate further, and you find that there is a chewing gum stuck inside the hole of the lock. And the key is not able to function.
Same thing happens in diabetes too. When insulin, the key, is not able to open the lock. And what is the chewing gum blocking its work? It’s fat. Fat makes insulin ineffective to do its job properly. Even a few extra kgs of weight can interfere with insulin’s ability to carry glucose into our cells. And this phenomenon is called insulin resistance.
There are multiple reasons why fat affects the work of insulin. In simple language, fat coats the cell membranes and impedes insulin function. Fat cells also produce binding proteins that get attached to the insulin, thus affecting its activity. Basically, weight makes the “insulin key” less efficient and you need greater number of “keys” to perform the same amount number of tasks.
Lipid overload leads to damaged mitochondria, which is also called the powerhouse of the cell. Mitochondria plays a vital role in conversion of food into energy for biological processes. A damaged mitochondria in turn leads to internal inflammation. And inflammation leads to insulin resistance. Hence, it is extremely important to lose extra weight to reduce insulin resistance.
Insulin is a Weight Gain Hormone
Insulin is a weight gain hormone. The job of insulin is to store glucose in your cells, and excess of it then converts into fat. More insulin in the body typically leads to increase in weight. If you want to reduce weight, your effort has to reduce overproduction of insulin. But in Type 2 diabetes, it leads to complications because of insulin resistance. As insulin is not performing to its optimal capacity, you need to produce more insulin to keep your sugar in control. And more insulin means higher weight gain. And higher the weight, higher insulin resistance and hence even more insulin is required.
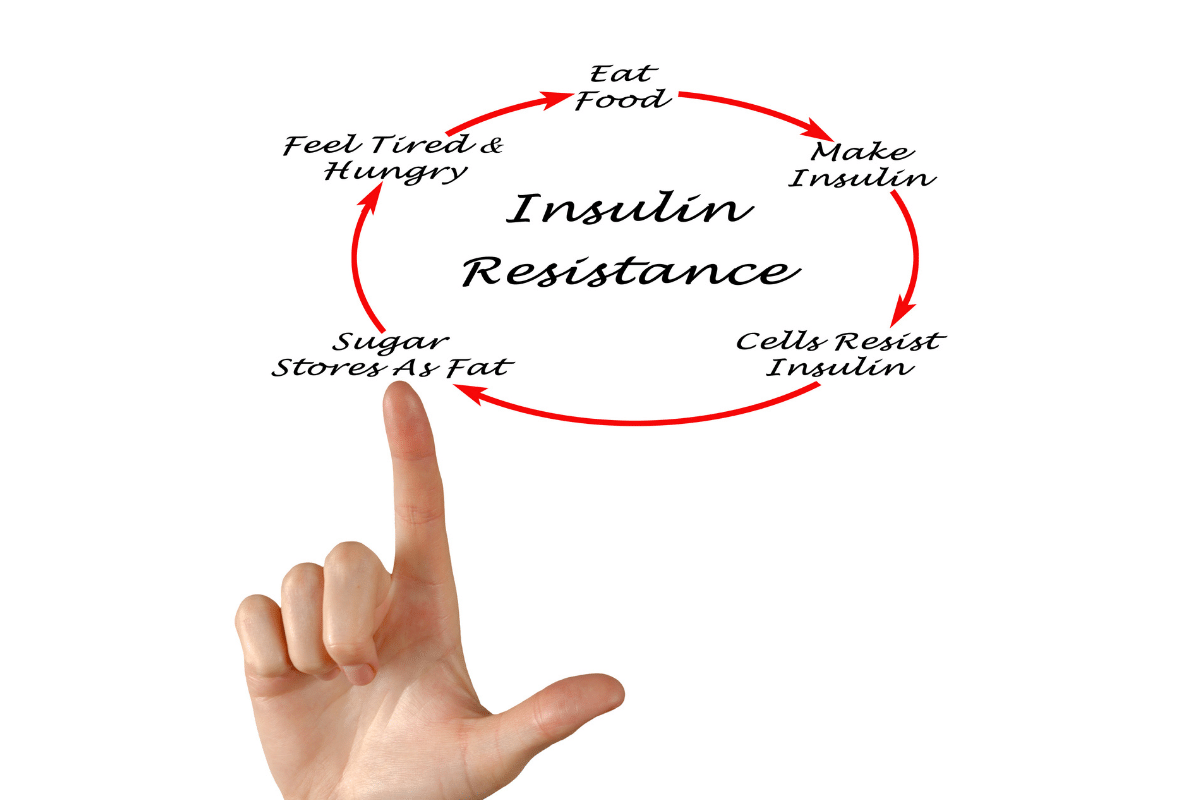
If being overweight is the significant causative factor in diabetes, then all efforts have to be made to reduce weight. But many medications focus on injecting or producing more insulin, which leads to weight gain. So, higher insulin in the short term will lead to lower sugar levels, but in the long term, aggravate the problem more by increasing your weight. And in turn make you more insulin resistant.
The solution to Type 2 Diabetes management is not to increase insulin production, but to make you less insulin resistant. One needs to increase the efficiency of existing insulin, and not increase the production of insulin.
Is it Difficult to Lose Weight In Diabetes?
In type 2 diabetes treatment, generally, your body requires more insulin. And insulin is a weight gain hormone. Therefore, the normal tendency for the body is to gain weight. Hence, it is slightly more difficult for a diabetic to lose weight. But most of the people lose 1-2 kgs per month, depending on the severity of the problem. Weight loss is a complex thing and not every person reacts in the same fashion. Hence, it is extremely important to be patient and give our 100% to see results. Healthy eating is not a temporary thing and is a lifelong habit. Sometimes results take time, but results always, always and always show up in the long term.
If you want to control or prevent diabetes, you need to be closer to your ideal body weight. David Marrero, PHD, President of Healthcare and education for the American Diabetes Association says, “What we know in diabetes prevention and in pre-diabetes, is that a very modest amount of weight loss has this huge reduction in risk. You lose 7% of your body weight, you cut your risk by 60-70%.” According to American Diabetes Association, losing even 4.5 to 6 kg weight can result in reduction in blood sugar levels and decrease in blood pressure.
Dr. Joel Fuhrman writes in his book “End of Diabetes”, “Through working with thousands of patients, I have observed with consistency that losing body fat in conjunction with maintaining high levels of micro-nutrients in the body’s tissues will reduce the need for medications and, in most cases, reverse Type 2 diabetes for good.”
Conclusion
Excess body weight is a leading cause for type 2 diabetes. And even losing 5-10% of your body weight can lead to a significant improvement in diabetes parameters and reduce risk of other complications. So, let’s take a pledge today to make Earth Lighter and Healthier. It’s Possible.
