Health, Lifestyle, Weight Loss
Sleep – The Key For A Stress Free Living
Medically reviewed by Dr. Shunmukha Priya, Ph.D. in Food Science and Nutrition
Medical professionals and scientists have time and again stressed that it is crucial to get a minimum of seven to eight hours of sleep. Not getting enough sleep will have long term implications on physical and mental health.
Table of content
- What is sleep?
- Stages of sleeping
- Benefits of sleeping
- What are sleep disorders?
- Causes and symptoms
- Sleep and weight gain
- Tips to improve sleep
- Conclusion
Despite this insistence, many of us tend to compromise on a good night sleep thanks to the stressful and shift based working hours this lifestyle brings and other entertainments like late-night outings that we often priorities first over our mental wellness. [1]
All the above-mentioned factors play a role in affecting our sleeping pattern. Our lifestyle choices have given rise to several sleep disorders in the recent past and are continuing. In fact, occurrences of disorders like insomnia and sleep apnoea are now common among all age groups.[2]
Well, before divulging into this article, let us give you a brief about sleep and what happens to the body when you sleep.
What is sleep and why it is important?
Sleep is an important biological process.
When we sleep, our body rests. It conserves the energy, decreases blood pressure, heart rate, breathing and body temperature. Even while sleeping, our brains are active – preserving memory and daytime mental functioning, as well as carrying out processes that are responsible for physical growth.
A night of good sleep is extremely important for functioning the next day. It keeps you refreshed and boosts your energy. Studies have shown that a well-rested mind has better focus and can solve problems more quickly than a sleep-deprived mind.[3]
The stages of sleeping
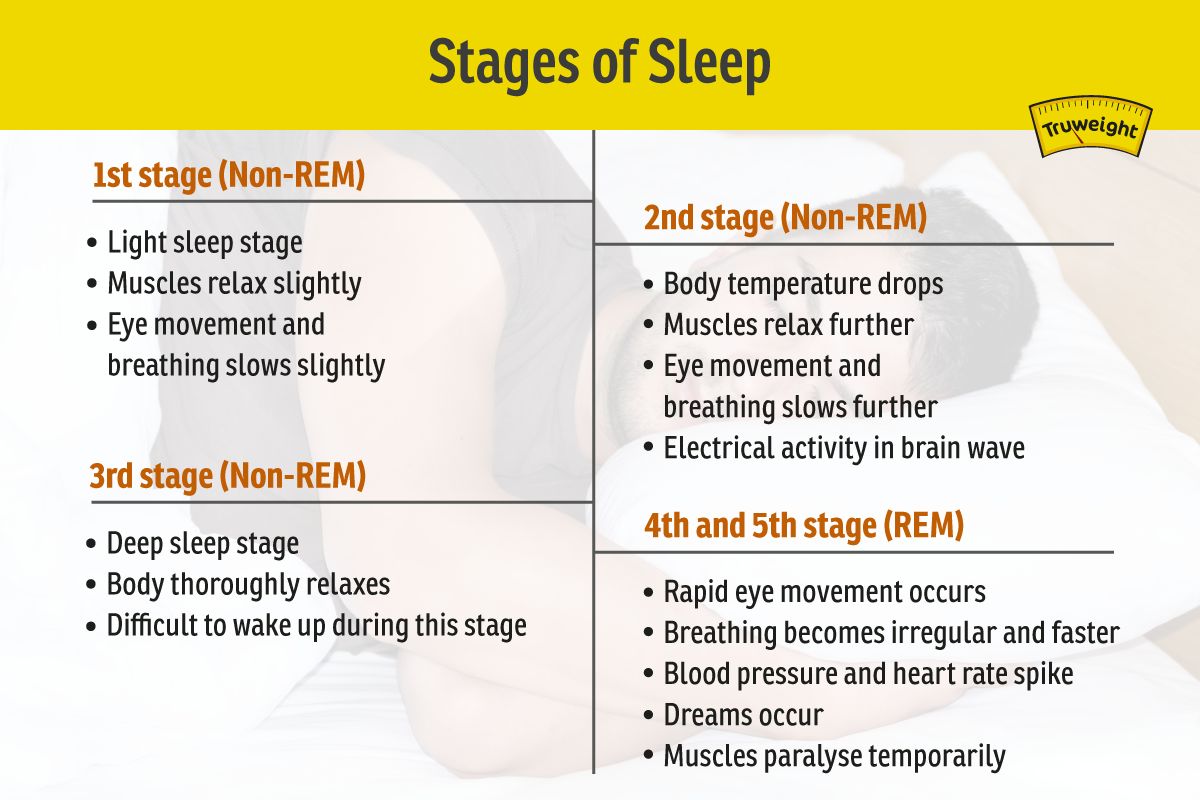
There are five stages in sleeping. It progresses from stage 1 (light sleep) through stages 3 and 4 (deep sleep) to stage 5 known as rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
Sleep is of two main types: Non-REM and REM. Each type is linked to particular neuronal activity and brain wave.
Non-REM
Non-REM has three stages to it.
- In the first stage, your body enters ‘sleep-mode’ after being wakeful for the entire day. During this stage of light sleep, your eye movement, heartbeat and breathing will slow down. Your muscles will relax and will twitch occasionally. The brain waves will also slow down.
- The second stage is also a light sleep stage that the body goes through before entering deeper sleep. Apart from the body relaxing further, body eye movement stops and body temperature drops. Brain wave will experience brief electrical activity in this stage.
- In the third stage, the body experiences deep sleep. This stage is crucial for the body to feel refreshed after waking up. This happens for longer period and your body is totally relaxed. Waking a person in this stage is difficult.
REM sleep
It is the final two stages of your sleep. REM occurs in 90 minutes after falling asleep. There will be rapid eye movement and your brain wave frequency will be similar to that of being awake.
During this stage, your breathing will become irregular and faster, blood pressure and heart rate spike up as well. Dreams usually occur during this stage and the body muscles become paralysed temporarily so you don’t act out your dream.[5]
Benefits of sleeping
There are some important processes that body undergoes while sleeping. Good night’s sleep does the following:
- Controls your body temperature, metabolism and energy expenditure.
- Ensures proper functioning of the immune system.
- Controls the brain functioning and saves and restores your memory.
- Keeps your heart and blood vessels healthy.
- Controls your blood glucose levels and insulin sensitivity.
- Repairs tissues and stimulates growth in children (growth hormone released during sleep is responsible for both). [6]
What are sleep disorders?
Conditions that interfere with regular sleep patterns are called sleep disorders. Though there are different types of sleep disorders, some of the major types are:

- Insomnia: This is a very common condition. You will find it hard to fall asleep or remain asleep during the night. Factors like caffeine intake, medications, stress, health conditions like depression and anxiety and jet lag play a role in this. Most insomnia cases can be cured by changing lifestyle and sleeping habits.
- Sleep apnoea: While sleeping, breathing stops temporarily and forces you to wake up frequently during the night. Though you will not recall waking up, you will feel tired, depressed and irked the next day. Whilst this disorder is treatable, it is still a life-threatening condition. It is best to see a sleep specialist immediately.
- Narcolepsy: Also called as ‘excessive uncontrollable daytime sleepiness’, is caused by the dysfunction of the waking and sleeping mechanism in the brain. You may fall asleep suddenly in the middle of the day irrespective of the task you are doing. A combination of treatments may alleviate the symptoms. A cure has not been found for this condition.
- Restless legs syndrome (RLS): As the name suggests if you have RLS, you will have the urge to move your legs while sleeping. You will experience uncomfortable, creeping and tingling sensations in your legs.
- Parasomnia: If you have this disorder, you may act unusually while sleeping, like sleepwalking or talking and waking up abruptly during the REM stage because of nightmares or night terrors.
- Circadian rhythm disorder: If you have this disorder, you will encounter problems with your sleeping and waking cycles. This disrupts your sleeping and waking times.[7]
Causes and symptoms of sleep disorders
Though the actual causes of sleep disorders are not yet known, here are some of the factors that contribute to these conditions.
- Too much of alcohol and caffeine intake
- Irregular work schedules (night shift)
- Ageing since older people do not experience the REM stage as their younger counterparts. Hence, they wake up quickly from their sleep.
Each sleep disorder exhibits different symptoms. Some of the common symptoms are:
- Waking up often in the middle of the night and finding it difficult to go back to sleep.
- Experiencing vivid dreams while sleeping.
- Feeling drowsy and falling asleep at the wrong time in the daytime.
- Tingling and creeping sensations in the legs during evening and night.
- Experiencing sudden weakness in muscles when exhibiting an emotion like laughing or feeling angry.
- Having difficulty in moving your body while waking up in the morning.
- Taking more than 30 minutes to fall asleep during the night.
- Your partner says that you snore, jerk your arms and legs, gasp, snort, choke while sleeping or stop breathing for a brief period.[8]
Sleep and weight gain
The human body is the most complex ever-evolving machine ever conceptualised. Any disruption to its natural cycle has multifold implications.
Less sleep or fragmented sleep affects a lot of things in our body that directly affect our weight. If you don’t sleep well, it almost directly affects your weight.
A study, cited by Harvard noted that there is a correlation between sleeping pattern and body weight.
According to the research conducted by the study, women who slept less than five hours are likely to become obese by 15% while compared to women who slept for 7 hours.[9]
Harvard study also observed that lack of sleep saps the body’s energy-giving little chance for incorporating physical exercises.
People who stay up at night for too long are hungrier and tend to too much food. Several studies also noted that sleep deprivation meddles with hormones that are responsible for appetite.[10]
Lack of sleep also affects a number of factors that are directly responsible for weight gain. These factors are:
1. Immunity
Sleep deprivation is linked with hormones that suppress the immune system. Researchers have found that a good night’s sleep can boost the effectiveness of certain specialised immune cells called T cells.
So, sleep loss not only plays a role in whether we come down with a cold or flu, but it also influences how we fight illnesses once we come down with them.
A large two-week study monitored the development of the common cold after giving people nasal drops with the cold virus. It was found that those who slept less than seven hours were almost three times more likely to develop a cold than those who slept eight hours or more.[11]
2. Hormones
Sleep deprivation affects your hormones.
When your body does not get enough sleep, your body has very little Leptin (a hormone that burns fat) and high Ghrelin (a hormone that promotes hunger). This causes the body to think that it is hungry and needs more food calories.
A study of over 1,000 people found that those who slept for short durations had 14.9% higher Ghrelin levels and 15.5% lower Leptin levels than those who got adequate sleep.
Also, Cortisol the stress hormone is higher when you do not get adequate sleep. Cortisol may also increase appetite.[12]
3. Gut -Bacteria
Recent research shows that not getting enough sleep can quickly have a negative effect on gut bacteria health.
In 2016, Swedish and German scientists conducted research on healthy, young, normal-weight men with no sleep disorders.[13]
After just two nights of partial sleep deprivation, scientists discovered:
- A notable decrease in the range of good bacteria.
- Changes to the composition of microorganisms in the gut that are linked specifically to obesity and type 2 diabetes.
- Insulin sensitivity was decreased.
We have already discussed how important gut-bacteria balance is to maintain a healthy weight and body.
4. Metabolic Health
Poor sleep also affects your body’s metabolism. Studies have noted that very little or restless sleep leads to changes in body metabolism.
It has a profound effect on eating patterns that increase the risks of obesity, type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
In a study that was conducted on healthy young men, restricting sleep to just four hours a night for continuous six nights caused symptoms of prediabetes.[14]
It was noteworthy that these symptoms alleviated just after a week of improved sleeping hours.
Poor sleeping habits were also strongly connected to adverse effects on blood sugar.
It is shown that people who sleep for less than six hours are at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Sleep deprivation also affects one’s resistance to insulin, thus causing weight gain.
5. Inflammation
New research found that sleep disturbances and long sleep duration are associated with increases in markers of inflammation.[15]
Both too much and too little sleep seems to be associated with inflammation, a process that contributes to obesity as well as many other health issues.
6. Stress
You have probably experienced it yourself that sleep affects mood. After a poor night’s sleep, you may feel more stressed, irritated and short-tempered. After sleeping well, your mood often improves.
Studies have noted that even partial sleep deprivation can have a profound effect on your mood.
A study conducted by the University of Pennsylvania found that participants who were limited to just 4.5 hours of sleep per night for a week reported feeling mentally exhausted, angry, stressed and sad.
When the participants resumed normal sleeping pattern, they reported a dramatic improvement in their mood.[16]
7. Digestion
Sleep deprivation also has significant changes in our body. People who do not get enough sleep are likely to complain about an upset stomach, diarrhea, body aches and acidity.
8. Appetite
Studies have shown that people who are sleep deprived will experience an increased appetite. It is believed to disrupt the regular functions of the appetite hormone. [17]
Lack of sleep increases the Ghrelin hormone and suppresses the Leptin hormone.
9. Fix your sleep
You have your own Circadian rhythm. Your body will tell you when it wants to or rather needs to sleep.
Sleeping for around 8 hours at least every day is important for optimum health. You may be an early sleeper or a late sleeper, suit your schedule. But don’t ignore this very vital aspect of life.
The next important thing to learn is how to sleep better. There are various theories around this too. Some resort to light music, some aromatherapy, some reading, breathing exercises at the time of sleeping etc.[18]
Here are some of the tips that you can adopt before calling it a night!
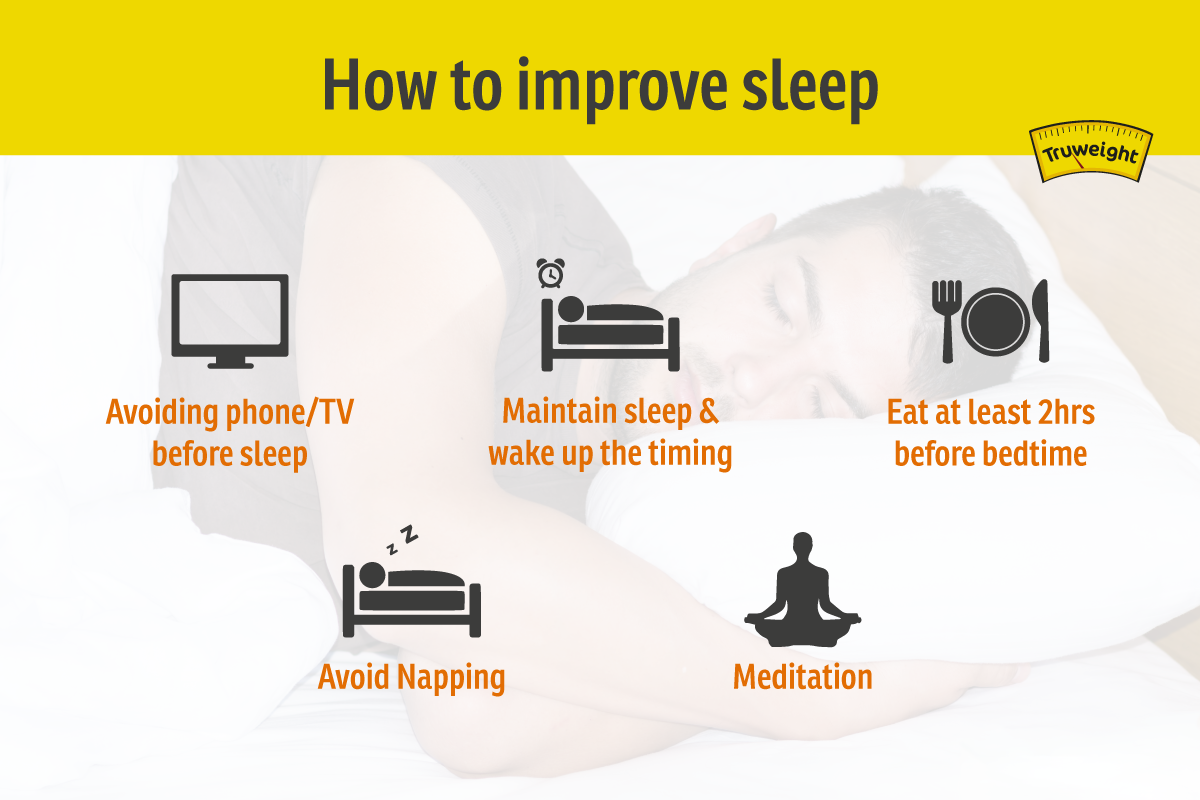
- Prioritize Sleep: Lifestyle is a new religion, and when you start following it religiously, you would have to make sacrifices. Limit late-night parties and movies. Prioritize sleep and plan the day accordingly. It also helps to have a family and social circle that sleeps early too!
- Maintain Timing: We are creatures of habit and so is our body. Respect the timing. Feed your body the same information at the same time daily and it will love you back. Try going to bed at the same time every day.
- Be active during the day: Lazing around the whole day will not help you get a good night’s sleep. It’s essential to keep your mind and body active during the day. Plan your day in advance and pack it up with meaningful things.
- Practice meditation or deep breathing: This helps relax your mind and keep you calm. The 5-5-5 breathing technique is quite handy. Take 5 deep breaths, 5 times a day, holding for 5 counts each.
- Eat 2-3 hours before bedtime: Eating 2 hours before going to bed will help release the right hormones and help you sleep better.
- No electronics rule: Bright visuals and strong sounds right before bedtime tend to stay in your memories and haunt your dreams or nightmares. Avoid watching television right before bedtime. A relaxed steady mind before sleeping will lead to a relaxed steady sleep.
- Put your phone away: Avoid using the phone right before bedtime. Put your phone in ‘night mode’ or ‘reading mode’. This silences the calls/messages and reduced the phone’s brightness making the device less exciting.
- Keep a watch or clock handy: If for some reason, you get up in the middle of the night, you obviously want to know the time. Do not pick up your phone to see the time. Keep a watch on your nightstand and pick that. There is no temptation to check anything else. See the time and close your eyes right after.
- Fresh air before going to bed: Try going for a stroll if it’s convenient and weather permits. Else, at least stand for a few minutes near the window or at the balcony/garden without your phone in hand. Take a few deep breaths and inhale some good fresh air.
- Wash your feet: Before you get to bed, take 5 minutes to wash your feet thoroughly with cold water. This will be quite relaxing.
There is absolutely no denying the fact that Sleep plays a vital role in good health and well-being throughout your life. Sleeping for a minimum of 8 hours will ensure great physical and mental health, safety and improves quality of life.
Most of the ‘sleep disorders’ that we encounter these days are a by-product of a stressful lifestyle. Altering your lifestyle will dramatically improve your sleeping habits. Joining a yoga class or doing some stretches before bed can help you relax and calm your nerves.
Conclusion
Sleep is a natural process and is very much related to one’s daily performance. It’s vital for an individual’s overall health and wellbeing. Lack of adequate sleep can cause problems like simple tiredness to complex metabolic disorders.
So, make sleep your first priority and watch your overall health falling into place! Happy sleeping!
*If you are not able to sleep due to mood disorders or finding it difficult to sleep despite altering your lifestyle, talk to a health professional or sleep specialist immediately to eliminate/treat any serious sleep disorder.
FAQs
Q: How to stop snoring?
A: Making lifestyle changes like losing weight, avoiding alcohol before bed time, getting enough sleep and clearing up nasal congestion can help stop snoring.
Q: How to sleep better?
A: Maintaining a consistent sleeping and waking time will improve your sleep. Similarly avoiding caffeine during the night and reducing napping will help you sleep better at night.
Q: How to cure a sleep disorder naturally?
A: ‘Curing’ a sleep disorder totally depends on the nature of the disorder. Disorders like sleep apnea needs immediate medical attention. Disorders due to poor lifestyle can be rectified by changing your lifestyle and sleeping habits.
Q: Are sleep disorders hereditary?
A: Some studies have discovered that disorders like Insomnia, Parasomnias and Narcolepsy are hereditary.[19]
Q: Can sleep disorders cause depression?
A: Sleep deprivation can alter one’s mood and several studies have linked depression to sleep disorders. If you think you have depression or have shown signs of depression, it is best to immediately talk to a specialist.
Q: How to overcome sleep disorder?
A: If you have trouble sleeping at night, it is ideal to talk to a sleep specialist. He/she will treat you or suggest changes in your lifestyle and sleeping habits to improve your condition.

Trueweight is literally the BEST weight loss blog anywhere, I read it every day, and I’m also so grateful, it helped me not only lose weight but keep it off, hope it helps some others!
Hi! Thank you for your lovely note, We are so gleeful to receive your feedback towards our blog, We are glad to know that our blog was very useful to you. Keep following our blog to know such more health information.